GUIDE: Physical, Medical and Dental Examination (PMDE) for PNP Applicants
GUIDE: Physical, Medical and Dental Examination (PMDE) for PNP Applicants
Congratulations for passing the Neuro-Psychiatric Exam (considered as the hardest test in the recruitment process).
Now, let’s proceed to the next phase of the recruitment, the PMDE or the Physical, Medical and Dental Examination. Under this phase, the PNP Health Service is in-charge/task to determine whether or not the applicant is in good health, free from any contagious diseases, a physical and medical examination.

On the first day of the PMDE, the applicants are required to fill up the Medical History Report and Medical Prescreen Questionnaire distributed by the RHS personnel purposely to record all information of applicant’s health. Through this report, the PNP doctors/examiners may now have an overview of medical condition of the applicant/s as to whether or not he is undergoing treatment or suffering from disease.
The Medical History Report may include information about allergies, illnesses, surgeries, immunizations, and results of physical exams and tests. It may also include information about medicines taken and health habits, such as diet and exercise. A family medical history includes health information about a applicant’s close family members (parents, grandparents, children, brothers, and sisters). This includes their current and past illnesses.
The
applicant must secure a copy of the PNP Applicants ID, attach a PASSPORT SIZE
ID Picture with Name-tag in white background and have it laminated. This ID
will be a requirement during the conduct of PMDE.

The following are the physical, medical and dental test:
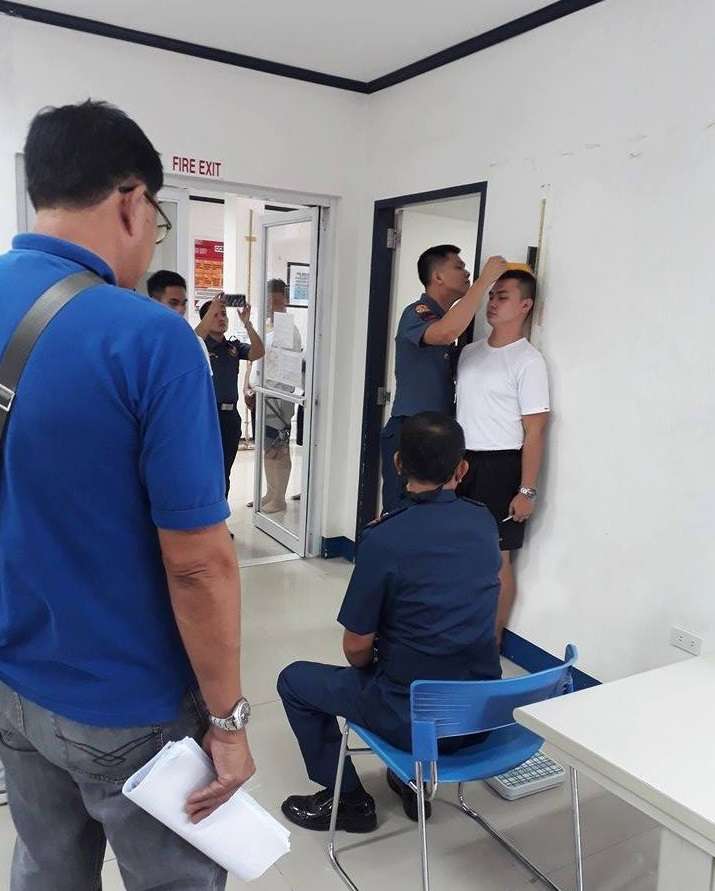
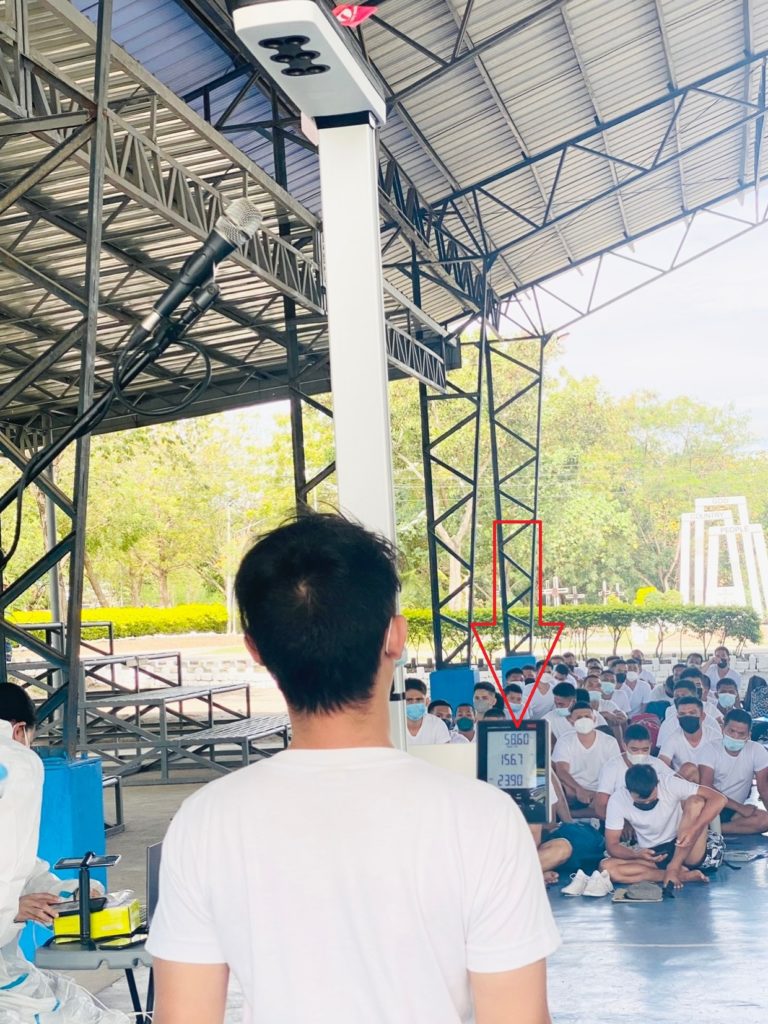
1. Height and Weight


PNP APPLICANTS | |
NOT ACCEPTABLE | < 18.5 |
ACCEPTABLE RANGE | 18.5-25.5 |
NOT ACCEPTABLE | > 25.6 |
BODY
MASS INDEX COMPUTATION
Based
on G. J. Hamwi Formula
48 kg +
2.7 kg per inch over 5 feet (male)
45.5 +
2.3 kg per inch over 5 feet (female)
Based
on J.D. Robinson Formula
52 kg +
1.9 kg per inch over 5 feet (male)
49 kg +
1.7 kg per inch over 5 feet (female)
IDEAL
BODY WEIGHT COMPUTATION
Body Mass Index Formula
Weight in kg over height in meter squared
To
illustrate:
Patrolman
Applicant Cardo Dalisay
Height
5’4” = 162.5 cm
Weight
67.5 kg BMI = 25.5
His ideal
body weight for his height:
Based
on Hamwi
48 kg +
2.7 (x 4 in) kg per inch over 5 feet = 58.8 kg
Based
on Robinson
52 kg +
1.9 kg (x 4 in) per inch over 5 feet = 59.6 kg
If
based on Hamwi
+/- 5kg
= 53.8 to
63.8 kg for a 5’4” male
(Equivalent BMI 20.37 to 24.16)
If
based on Robinson
+/- 5kg = 54.6 to 64.6 kg for
a 5’4” male
(Equivalent BMI 20.68 to 24.47)
If based on BMI set at 25.5 his expected weight is 67.5 kg
2. Ear Nose Throat Exam (ENT)

3. Chest X-Ray PA view
NOTE: Tuberculosis is a
highly contagious bacterial infection that can quickly spread under certain
conditions. It is an airborne disease, and can be caught by breathing in the
air that an infected person has contaminated through: Breathing, Coughing, Talking
and Sneezing. So as much as possible, applicant should be cautious about dealing with other co-applicant because every
recruitment cycle there will always be applicant who found positive in
tuberculosis.
4. Electrocardiogram (ECG) is a test that measures the electrical activity of the heart.
5. Urinalysis
test – is used as a screening and/or diagnostic tool because it can help detect
substances or cellular material in the urine associated with different metabolic
and kidney disorders. It is ordered
widely and routinely to detect any abnormalities that require follow up. It is
used to detect urinary tract infections (UTIs) and other disorders of the
urinary tract. In those with acute or chronic conditions, such as kidney
disease, the urinalysis may be ordered at intervals as a rapid method to help
monitor organ function, status, and response to treatment.
6. Blood
Chemistry Examination
a. Fasting Blood Sugar
(FBS)
b. Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN)
c. Creatinine

7. Snellen
test – 20/20 or 6/6

8. Ishihara test or color perception test. You can practice ONLINE

Color
blindness is not a form of blindness at all, but a deficiency in the way you
see color.
If you are colorblind, you have difficulty distinguishing certain colors, such as blue and yellow or red and green.
Color blindness (or, more accurately, color vision deficiency) is an inherited condition that affects males more frequently than females. According to research, an estimated 8 percent of males and less than 1 percent of females have color vision problems.
Red-green color deficiency is the most common form of color blindness. Much more rarely, a person may inherit a trait that reduces the ability to see blue and yellow hues. This blue-yellow color deficiency usually affects men and women equally. (Source: https://bit.ly/2rAOTST)
9. GPE or General Physical Exam – body check-up such as scars, tattoos, varicose veins, hemorrhoids and hernia are grounds for disqualification.
At this stage, the applicants are required to perform PNP dozen exercise/s and to run 3 to 5 rounds (oval) prior to the conduct of GPE.

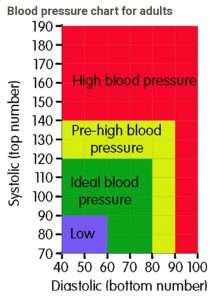
Blood
Pressure (BP) Screening
If
your blood pressure is high at one reading, that doesn’t mean you have high
blood pressure. Blood pressure can vary depending on your activity level and
time of day, and can be higher if you are sick or in pain.
Blood
pressure is measured using a device called a sphygmomanometer. Usually you are seated with your arm resting on a
table. A cuff is placed around your upper arm and inflated until it stops the
blood flow. Then the cuff is slowly deflated, allowing blood to flow again. As
the cuff deflates, a stethoscope is used to listen to the blood flow in an
artery at your inner elbow.
The
first thumping sound heard reflects the blood pressure as the heart contracts (systolic pressure). When the thumping
sound disappears, this is the lowest amount of pressure (diastolic) between heartbeats. Some use automated machines which
take blood pressures. (Source: https://k-p.li/2JZmzmB)
Preparing for your
screening
To
prepare for a blood-pressure screening, follow these guidelines:
–
Don’t smoke or have caffeine for 30 minutes before the test.
– Rest for at least 5 minutes before the test.
– Sit in a chair with your back and feet supported, and your arm supported at heart level.
READ
ALSO:
PNP Recruitment
Process (UPDATED)
10. Dental Exam -Full dentures upper and lower are disqualified.
11. Other
laboratory examinations as requested by attending physician/s to aid in the
diagnosis of diseases or determination of status of medical condition of an
examinee. It also includes second opinion from other private or public medical laboratory
referred by the PNP Health Service. However, the Pregnancy Test for female applicants is
conducted on or at least one day before taking oath.
Grounds for DISQUALIFICATION
(DQ)
TATTOs
Current tattoos of any size in any part of the body except for aesthetic enhancement (e.g. eyebrow tattoo).
UNDERWEIGHT AND OVERWEIGHT
Failure
to comply the standard BMI is tantamount to disqualification.
ECG ABNORMALITIES
The
following ECG findings may be ACCEPTABLE only after further evaluation
and only in THE ABSENCE OF AN ORGANIC HEART DISEASE.
Left
Ventricular Hypertrophy
Right
Ventricular Hypertrophy
Left
Atrial Abnormality
Right
Atrial Abnormality
Left
Anterior Hemiblock or Left axis Deviation
Left
Posterior Hemiblock or Right axis deviation
First
degree AV Block
Poor R
Wave Progression
Persistent
Posterobasal Forces
Early
Repolarization Pattern
Incomplete
Right Bundle Branch Block
Interventricular
Conduction Delay
Sinus
Bradycardia
Sinus
Tachycardia
Sinus
Bradyarrythmia
Sinus
Arrhythmia
Non-specific
ST Wave Changes
Septal Wall Ischemia
Anterior Wall Ischemia In Females
DEFECTIVE VISUAL
PERCEPTION
(color
blindness, near sighted/far sighted with corrective eyeglasses or lens, nystagmus);
Full
dentures, Cleft lip and palate, malocclusion, Deformities of the face, Open
bite, Speech defect, four(4) missing front teeth and/or six (6) posterior/molars;
Perforated
ear drum, chronic sinusitis, bleeding tendencies, hemorrhoids (almurans), hernia/luslos (if not
treated), varicocoele, extensive skin disorders;
Congenital Diseases, Communicable Diseases Etc; (TB, HEPA B, etc)
This
phase may take 2-3 weeks or even a month depending on the number of applicants.
The health service personnel are expected the applicant to be at the area from
7am (assembly/formation time) to 5 or 6pm. Just a tip though, always prepare a
song/dance move or any skills during “happy hour” or we called it as “PROLEX.”
Stay
your feet on the ground and never outshine the master.
Good LUCK And GOD BLESS!